Project Outline
- Aims and Objectives
- Integration of the curriculum
- Improved learning through engagement
- Embedding (and dissemination)
- Outcomes
- The Project plan
- The project timescale
- Management structure
- Evaluation strategy
- Dissemination
- Communication channels
- Internal dissemination
- External dissemination
- Continuation
- Stakeholder involvement
Aims and Objectives
Integration of the curriculum
Initially this will be achieved through providing a common context within which the different aspects of the subject are presented and resources on which the different disciplines will draw. In the longer term, it is intended that the resource will be embedded more centrally in to the structure of the first year and this is the aim forms part of the dissemination strategy for the project.
The success of the resource will be assessed against the following factors as part of its evaluation:
| Success factors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Scope | provides appropriate opportunities for supporting the aims of modules in: | |
| marketing | ||
| HRM | ||
| operations | ||
| information management | ||
| finance and accounting | ||
| environmental aspects | ||
| ethical aspects | ||
| strategic aspects | ||
| as well as linking them together | ||
| Currency | contains up-to-date information about the company and its environment | |
| is easily updatable | ||
| reflects current business and management practice | ||
| Connectivity | emphasises the holistic nature of the modern business | |
| demonstrates that changes in one area of the business will have implications on others | ||
| capable of joining up | ||
| Practical | resources are amenable to hands-on activity and are easy to manipulate | |
| circumstances are of direct relevance to the audience | ||
| effects of intervention can be seen directly | ||
| Accessibility | physical nature of resources is attractive and engaging | |
| access to place – digital, on-line, hardcopy | ||
| access to time – as above plus synchronous, asynchronous engagement | ||
| variety – of students' educational experience (structure of learning environment), backgrounds, abilities, levels of confidence | ||
| disability aspects | ||
Improved learning through engagement
Through its content and coverage, the resource will bring reality and currency into learning and will enable the development of skills of analysis, problem solving, team working, researching and critically assessing information sources.
The main pedagogic approach on which this proposal is based is that of experiential learning (Kolb, K., 1984) and tutors will be able to choose ways of utilising the resource based on action learning (McGill, I and Beaty, E., 2001) and problem based learning (Boud, D and Feletti, G. I., 1997) approaches.
The success of this aspect of the project will be assessed against the following factors as part of the evaluation of the project:
| Success factors | ||
|---|---|---|
Integrative |
is used to demonstrate specific functional aspects within the context of the wider business |
|
|
is used across a range of different functional areas |
|
|
the same business circumstance can be considered form a variety of standpoints. |
|
Student-directed |
facilitates and motivates students. |
|
|
contains self-study material |
|
|
has multi-channel pathways? |
|
|
experiential learning - learning by discovery |
|
|
action learning |
|
|
project based learning |
|
Engaging |
attractive |
|
|
understandable |
|
|
relevant |
|
|
good access |
|
|
entertaining? |
|
|
multiple mode delivery |
|
Supportive |
provides backup materials when required |
|
|
provides feedback on progress |
|
|
access to tutor support |
|
Flexible |
variety of possible uses |
|
|
individual, group work possibilities |
|
Assessed |
it enables assessment and feedback on scope, currency, connectedness |
|
|
the learning material involve self/group/tutor assessment and feedback on knowledge and understanding |
|
|
can be used as part of the assessment of modules: |
|
|
either as part of the package of assessment for an individual module, |
|
|
or to jointly assess aspects of several modules together. |
|
|
assessment elements should also be student-directed, engaging, supportive, flexible |
|
Embedding (and dissemination)
The project plan includes the embedding of the resource locally. It will be evaluated and improved through the experience of working with it. The achievement of this aim will be facilitated by the involvement from the start of the leaders of the modules to which it can be applied.
Wider embedding will be sought through wide dissemination, firstly through cascade partners and through other means (see section 6).
The success of this aspect of the project will be assessed against the following:
| Success factors | ||
|---|---|---|
Evaluated |
is shown to be effective in respect of the objectives |
|
Widely disseminated |
wide interest in adoption |
|
|
number of events, publications, |
|
|
sizes of audiences |
|
Adopted (has impact) |
has been used: |
|
|
|
internally |
|
|
externally |
Embedded |
the extent to which the resource features in the mainstream delivery of the modules |
|
Outcomes
- company information and data: e.g. a company web site, annual reports and statements, transactional database, virtual tour, audio interviews with key management.
- learner support materials: e.g. structured guidance and learning activities with feedback that will enable students, both individually and in groups, through tutor-directed and self-directed study, to explore the significance of the studied subjects to the running of a business and to develop their descriptive and analytical skills.
- models for using the resource: the learning resource will be designed to enable modules to use materials in a way that serves the module's learning outcomes and to fit appropriately within their learning, teaching and assessment strategies.
The package will be designed to provide a rounded learning experience and will utilise a Virtual Learning Environment (VLE) for its delivery.
The success of achieving the outcomes will be assessed against standard project management criteria:
| Success factors | ||
|---|---|---|
On time |
all milestones achieved |
|
Within budget |
budget constraints observed |
|
To specification |
fit for purpose |
|
Efficient, effective, “value for money” |
has high impact at reasonable cost |
|
The Project Plan
The project timescale
The project will be undertaken over three years in five overlapping phases: design, development, implementation, evaluation and dissemination. This is illustrated in the figure below.
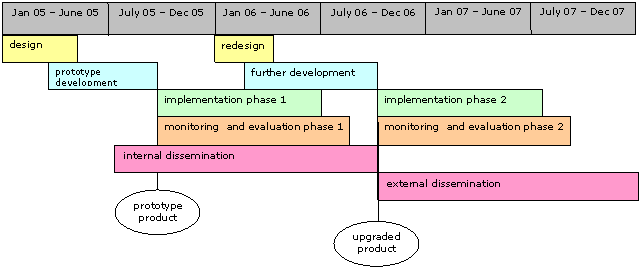
Outline project timescale
The completion of a prototype resource in time for the start of the academic year 2005-06 is a critical project milestone. It is intended that some preliminary work will take place during the preceding academic year in order to ensure the achievement of this milestone.
The phased approach represents an iterative development allowing the evaluation of piloting the prototype to inform further development of the product and the supporting resources.
The majority of the cost will be incurred by academic and support staff time and the phasing of the expenditure reflects the time devoted to design and development activity.
Management structure
The management structure is illustrated in the figure below:
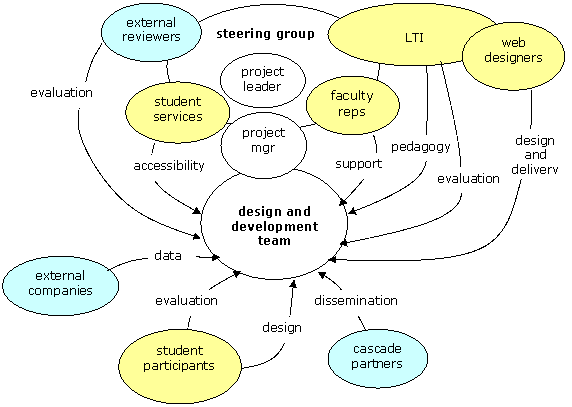
Management structure
The project design and development team will comprise the module leaders of the mandatory modules of the first year Business Studies programme and the project manager. Their role will be to first specify the roles for the resource so as to achieve the integrating and motivating aims for their modules and to then develop the resource to meet those roles. They will be responsible for the implementation and evaluation of the resource during the pilot and second pass of the implementation plan.
The project manager will coordinate these activities and report to the Steering Group. The project manager will be selected from amongst the module leaders on the design and development team and so will have a direct understanding of the project's aims and objectives.
The Steering Group will comprise representatives of the internal consortium will are critical to the project's success:
- The Learning and Teaching Institute (LTI) - will advise on pedagogy and evaluation and provide internal review,
- Student Services – will advise and evaluate the accessibility aspects of the project,
- Faculty representatives – will represent management and wider parts of the new faculty and will have an internal dissemination role,
- external reviewer – will review progress and ….
The Steering Group will be led by the Project Leader who will coordinate the work of the internal consortium who will also liaise with the external cascade partners at all the dissemination stages.
Evaluation strategy
The iterative nature of the development allows continuous monitoring and evaluation for improvement. The pilot stage of the project will be evaluated and the results will inform the further development of the resource.
The success of the product and pedagogic aims of the project will be assessed against the criteria listed in section 2 (Aims and Objectives).
The structure of the evaluation approach is shown below:
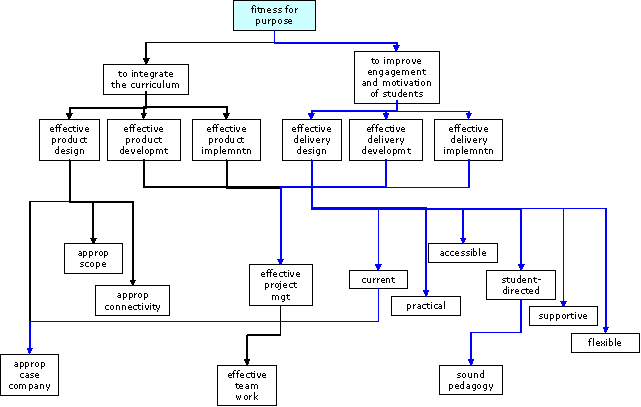
Evaluation structure
The project success will be monitored and reviewed through standard project management methods.
Further evaluation will take place through student feedback. As well as a continuous monitoring of the levels of engagement of students during the course of the project, employability aspects can be evaluated. The first cohort of students who encounter this resource will have progressed to their placement year at the final stages of the project. This enables an assessment of the effect on preparation for placement.
The dissemination aims for the project will be evaluated against a variety of criteria relating to impact in the wider field.
Dissemination
Communication channels
The communication channels that will be adopted for dissemination are illustrated in the fig below:
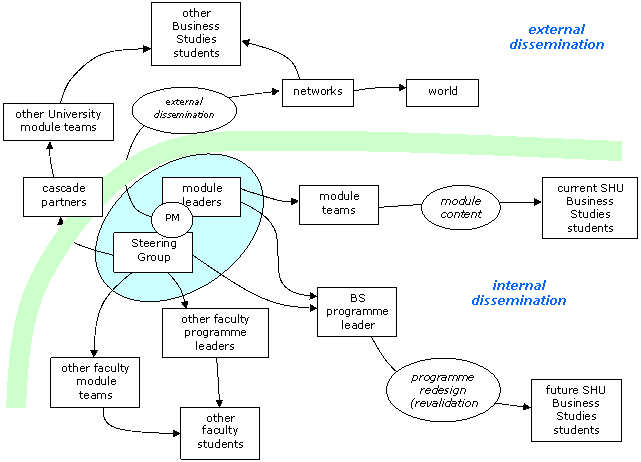
Dissemination model
Internal dissemination
The project will involve an internal consortium of subject areas and support departments currently located in different organisational units within the University. The very process of design, development and implementation will involve a wide variety of disciplines and support functions and will therefore enable adoption of the resource and embedding of the supporting pedagogy within the institution.
The project will serve to enhance the working relations internally in a number of ways.
- It will serve to foster collaboration between the subject areas within the discipline: the following subject areas will contribute to the development of support materials and will utilise the resource as part of their teaching: Business Operations, Marketing, Human Resources Management, Information Management, Strategy, Facilities Management. The CVs of module leaders in these areas are included.
- The development of the learning package will require a variety of expertise and will involve extensive cooperation between academic and support staff (for web design and resource production) within and outside the University. The University's Learning and Teaching Institute (LTI) will provide expertise in pedagogy and access to services essential to this development and will play a significant role in the dissemination of the outcomes from the project.
- The Learning Support Team from the Student Services Centre will provide a brokerage role to link the project with specialist services, including the Careers and Employment Team, the Disabled Student Support Team, and the International Adviser. This has the aim of sharing expertise on effective approaches to ensuring access and achievement for students from a wide variety of backgrounds. This is an innovative feature which we anticipate will be of interest to many institutions with similarly diverse student profiles.
Key personnel in these areas are listed as the co-applicants for this proposal and their CVs are provided.
The timing of the project would coincide with two significant events within Sheffield Hallam.
- The current School is undergoing a merger with other areas of cognate disciplines to form a faculty and this offers the opportunity for wider adoption within the new faculty.
- The undergraduate programmes are due for redesign and revalidation and there is scope for the principles underpinning this project idea to be embedded more systematically within the curriculum and structure.
The development of the company which sits at the centre of this resource will involve collaboration with a number of commercial companies. The network of collaborating organisations will be extended to establish stronger links between the commercial and business education worlds.
Continuation:
The resource can be embedded more centrally in the curriculum within a redesigned business programme curriculum. This subject area at Sheffield Hallam will be revalidating its undergraduate programmes in 2005.
External dissemination
The key mechanism for external dissemination is the network of “cascade partners” that will be established to take a role in design, piloting and evaluation. Additionally the network…
Evidence of the commitment of typical partners is given.
There are two outcomes of the project that will be disseminated externally:
- the resource and how to use it – this will involve awareness raising, improved understanding and implementation issues and will take place principally through existing business education networks, e.g. LTSN BEST, EDINEB, through workshops, conferences and seminars. The resource could be made available to a wider academic audience through Biz/ed. Professional bodies such as CIMA have expressed an interest in the dissemination of such a resource.
- the pedagogy that underpins the approach and the experience of having applied it – this will focus on implementation issues and will take place through forums involving our cascade partners, through publications, conferences and workshops organised through our network connections.
Continuation
The project has the potential for further development in a number of ways.
The resource can be embedded more centrally in the curriculum within a redesigned business programme curriculum. This subject area at Sheffield Hallam will be revalidating its undergraduate programmes in 2006-07.
The resource and the principles underpinning its use can be extended to other levels in undergraduate programmes (e.g. as a preparation for placement) and to postgraduate programmes.
The commercial value of such a resource can be exploited (within the conditions of the funding) to provide self sustaining development resources.
Stakeholder involvement
The table below summarises these dissemination aspects against the key stakeholders:
| Goal Focus | Internal | External |
|---|---|---|
| Awareness | Bus Studies module teams - will be involved in the pre-project briefing by module leaders who are on the project planning team Bus studies programme management - aware of resource design and model for integration through Steering Group involvement other faculty module teams - aware of resource design through Steering Group involvement Faculty management - growing awareness of wider potential through design and development phases LTI - involved in deciding pedagogic models to underpin delivery modes (development); through internal LTA conference Student Services - involvement with design Staff/student intranet |
Cascade partners – through involvement in design; Public website; Publications and flyers; LTSN ; EDINEB; Conferences; Discussion lists; Professional bodies (CIMA) |
| Understanding | Bus Studies module teams – will be consulted by module leaders during the design phase Bus studies programme management – understand the scope for systemic integration through development phase Other faculty module teams – understand the potential through development phases; Faculty management - potential for faculty wide strategy development during implementation 2 phase LTI - advising on application of delivery models Student Services – workshops for Faculties and Subject Groups |
Cascade partners – through piloting; |
| Action | Bus Studies module teams – will be actively engaged by module leaders during the development phase Bus studies programme management – evaluate the potentials for wider programme redesign and revalidation; Other faculty module teams – adopting resource as appropriate during implementation 2; evaluating impact on wider SHU faculty students and improving the application; Faculty management –designing and developing other faculty programme revisions LTI - evaluating the effectiveness of the delivery models Student Services - |
Cascade partners - institutional visits for workshops, consultancy, etc. |
| Embedding | Bus Studies module teams – will be delivering the resource during the implementation phases 1&2; monitoring and evaluating its application and impact on current SHU BS students Bus studies programme management – redesign curriculum Other faculty module teams – refining and further modification Faculty management – evaluating impact on wider SHU faculty students LTI - Student Services – embedding in institutional policy, strategy and practices working with course/module teams to embed |
Cascade partners – wider adoption |
| Continuation | Bus Studies module teams – will be feeding back evaluation and involved with ongoing development and refinement for impact on future SHU BS students Bus studies programme management – implementation of newly designed curriculum with impact on future SHU BS students |

